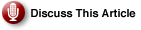Installing IIS 6.0 via the “Configure Your Server” Wizard
With that said, there are several ways to install IIS 6.0 on a Windows Server 2003 system.
|
Unsure About an Acronym or Term? |
The simplest way (which does not allow for much additional configuration as far as configuration options and secondary services like FTP or SMTP) is to configure the Application-Server-specific role for your system by using the “Configure Your Server” wizard.
To successfully run the wizard, you must be logged on to the local system with an administrator account (or any other account for which the required permissions and rights on the local system have been delegated).
Another installation option is to use Add or Remove Programs from the Control Panel. The next article in this series will detail that type of installation.
The recommended approach, as far as security is concerned, is to not log on to any systems with an administrator account but rather to log on with a domain (or local) user account and use the Secondary Logon service known as RUNAS to launch an application or an installation program only with the appropriate administrative rights to perform the needed function on the system. Once the program is closed, or the installation complete, the administrative context is released and everything else running under that user account on the system is running at the lower “user” level.
NOTES FROM THE FIELD — Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 225035, Secondary Logon (Run As): Starting Programs and Tools in Local Administrative Context, details the procedure. Although the article itself pertains to Windows 2000, the functionality is more or less the same as it is in Windows XP and Server 2003.
In summary, to start an application (such as CMD.exe) using Secondary Logon, go to Start, click Run, type runas /user:machine_nameadministrator cmd, where machine_name is the name of your computer, and then click OK.
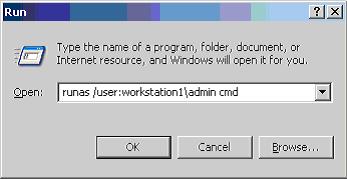
A console window will appear, prompting for a password for the machine_nameadministrator account.
Type the password for the administrator account and press ENTER.
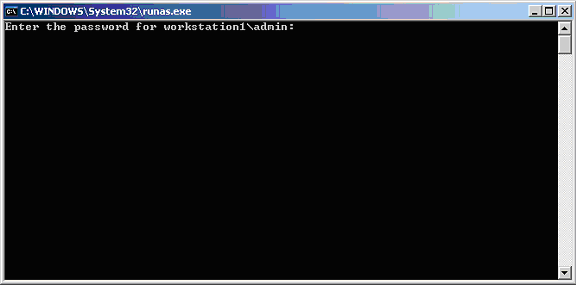
A new console will appear, running in the administrative context, as shown in the title of the console itself.
Any command-based programs can now be started from this console window and also run in an administrative context.
In addition, you can run an application from its shortcut by selecting the particular application’s shortcut from the desktop, the Control Panel, or the Start Menu, and holding down the SHIFT key and, once the icon is highlighted, left-clicking it one time.
Once it is highlighted, and while you are holding down the SHIFT key, right-click the icon to bring up the Run as … option in the right-click pop-up list.
A dialog box titled, “Run program as other user” will appear, which will allow you to enter the local or domain credentials required to start the tool or application in an administrative context.
One slight difference in Windows Server 2003 vs. what is outlined above for Windows 2000 and XP is that in Windows Server 2003 you need only perform the “hold the shift key down and right click” action to bring up the RUNAS option on the right-click menu for your Control Panel tools, whereas this must be done for everything in Windows 2000 and XP. Regular EXEs at their path location, Start Menu shortcuts, and shortcuts on the desktop will automatically show RUNAS on the right-click menu
without holding down the SHIFT key on Windows Server 2003 systems.
Original date of publication, 07/31/2003