This week we’ll continue our discussion on how
to troubleshoot common problems with Microsoft Proxy Server 2.0. Last week we
went over the basics of how the three Proxy Services worked, and some common
problems in Troubleshooting the Server configuration. If you missed it, you can
read that article by going HERE.
This week we’ll continue our discussion on how to troubleshoot common problems with Microsoft Proxy Server 2.0. Last week we went over the basics of how the three Proxy Services worked, and some common problems in Troubleshooting the Server configuration. If you missed it, you can read that article by going HERE.
This week we’ll cover issues related to the Web Proxy, WinSock Proxy and SOCKS Proxy Service. These are the core services provided with Microsoft Proxy Server and knowing the common headaches associated with them can save you some time should things go wrong.
This week we’ll cover issues related to the Web
Proxy, WinSock Proxy and SOCKS Proxy Service. These are the core services
provided with Microsoft Proxy Server and knowing the common headaches associated
with them can save you some time should things go wrong.
Common Web Proxy Service Problems
Many problems involving the Web Proxy service are
related to the security configuration of the IIS Server on which the Web Proxy
service depends. Remember, the Web Proxy service is an ISAPI plug-in to the IIS
Server’s WWW Service. You configure the type of security required to access
the Web Proxy service at the IIS Server console. Below you see the
authentication methods configuration interface on the IIS Server.
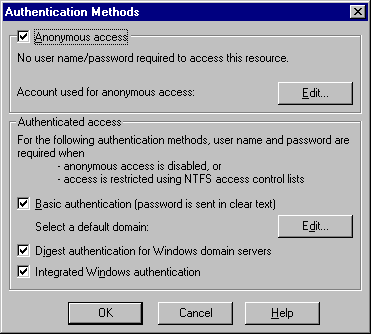
On this IIS 5.0 Server, you can see that all
three of the supported authentication methods are allowed: Basic
Authentication, Digest authentication and Integrated Windows
authentication. Keep in mind that Basic Authentication sends the username
and password in clear text and can be easily sniffed. Digest Authentication is
new with IIS 5.0. The IIS Server send some information to the client, and the
client browser will hash this information with the username and password. The
hash is sent to the server for authentication. The Integrated Windows
authentication is the same as the NT Challenge/Response authentication you used
in IIS 4.0.
When you see the following error:
HTTP/1.0 500 Server Error (-number)
It may be related to the use of Integrated
Windows Authentication. Change your authentication method to Basic
Authentication and see if problem goes away. If it does, you should consider
problems related to the use of NTLM on the network and perhaps consider using
only anonymous access, or Digest Authentication.
You can start and stop IIS integrated services
from the command line. The net stop and net start commands can be
used to quickly stop and start IIS services. For example, if you want to stop
the WWW Service, you could type at the command prompt:
net stop w3svc
To start it again, type:
net start w3svc
If you try to start the WWW service from the
command line, and you get an error such as:
An instance of this service is already
running
Its most likely because you’ve started the Web
Proxy Service already. Since the Web Proxy service is dependent on the WWW
service, when you start the Web Proxy service it will automatically start the
Web Proxy service.

