What Is VMware vSphere 7?
VMware vSphere is a hardware virtualization solution that allows system administrators to install and configure multiple virtual instances on a single host. Multiple virtual instances can be created with the help of a virtualization layer called a hypervisor.
A hypervisor abstracts the underlying hardware from the host and allocates it to the virtual instances called virtual machines (VMs). VMware introduced several releases and advanced features over time to fulfill customers’ requirements.
vSphere 7 is the most significant vSphere release in over a decade. VMware vSphere with VMware Tanzu enables system administrators to get started with Kubernetes workloads in less than an hour with the newest version.
VMware just released VMware vSphere 7 Update 3d, which fixes the CVE-2022-22948 vulnerability as well as problems with vCenter Server 7.0, including networking, server settings, vSphere HA and FT, security, and update issues. Monthly fixes for VMware vSphere with Tanzu are also included in this new release.
The latest edition of the virtualization software, vSphere 7, adds a slew of new capabilities. For version 7, VMware vSphere has been considerably “re-architected.”
In this article, we’ll go through the new features in VMware vSphere 7 that help you to determine if it’s worth switching to vSphere 7 or sticking with your existing vSphere version.
Read more: vCenter vs vSphere vs ESXi: Comparing VMware Virtualization
Capabilities and Major Features
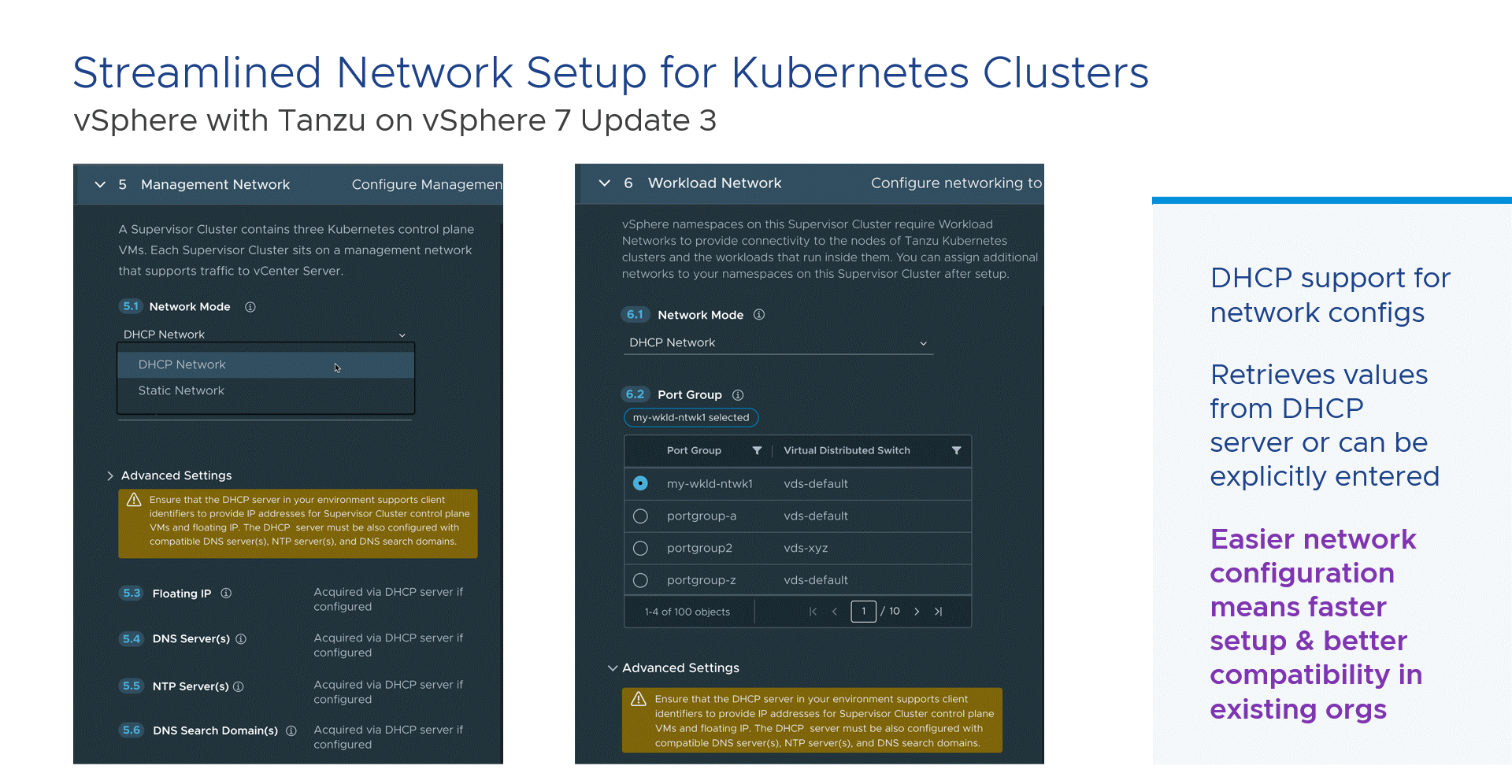
On March 29, 2022, VMware released vSphere 7.0 Update 3d, and it continues to add new features to each edition. vSphere 7.0 U3d is now available for download, and it includes several bug fixes from previous versions.
Some of the new advanced features in VMware vSphere 7.0 are listed below.
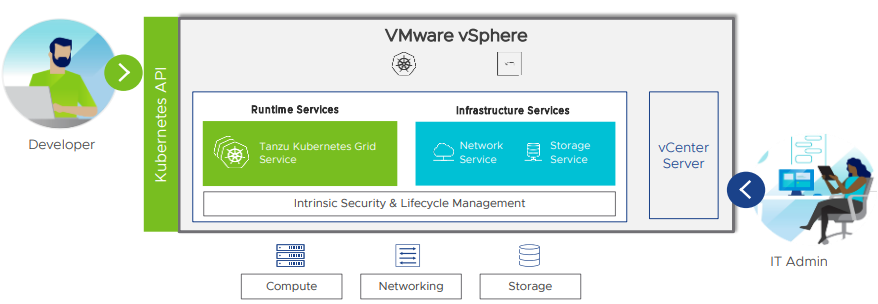
vSphere With Tanzu
One of the most essential elements of vSphere 7 is the integration of Kubernetes, which is called vSphere with Tanzu. It allows companies to quickly deploy and run container-based modern apps on top of their existing infrastructure.
Developers may quickly build clusters and deploy apps using standard tools and YAML files, providing good self-service capabilities.
vCenter Plugin for NSX
This plugin simplifies the configuration of NSX networking in VMware vSphere Client for system administrators. With the vCenter Plugin for NSX, you don’t need to log in to the NSX manager due to seamless authentication between vCenter and NSX-T.
It is more user-friendly to control settings in a single pane of glass owing to the integration of vSphere and NSX. Although, you’ll need an NSX-T license to utilize the plugin.
For distributed firewalling in NSX-T settings, you can use vSphere distributed virtual switches. This solution requires fewer network setup changes in vSphere and NSX.
DRS Improvements
The current DRS approach is to migrate large-sized VMs as little as possible. This method helps to reduce the chances of failure during maintenance, upgrades, and VM migrations.
DRS tries to transfer a large-scale VM from a maintenance mode server to an ESXi host running the most recent version of ESXi. The VM then continues to run on the host to which it was transferred without having to be migrated back (with VMware vSphere 7.0 Update 3, it is no longer necessary to move this VM back).
vCenter Lifecycle Manager (vLCM)
VMware formerly utilized vSphere Update Manager to manage updates for ESXi hosts, clusters, and vCenter servers. VMware has renamed this component to vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM).
vLCM keeps server hardware up to date and consistent. It keeps VMware Update Manager’s capabilities but adds a new intended state model that ensures that OEM-supplied server firmware is also kept up to date.
A few of the new features of vLCM include cluster software management using desired state images, host hardware verification against the VMware Compatibility Guide and the vSAN Hardware Compatibility List, and the ability to conduct automatic firmware updates.
VMware Virtual Hardware 19
The newer VMware vSphere 7.0 Update 3d, which is compatible with VMware Virtual Hardware version 19, was just released. Virtual hardware version 19 provides additional features and capabilities such as 24,512 GB RAM, 768 logical processors, 64 vCPUs, and VMware vSphere 7.0 U2, and subsequent versions are compatible.
To assess whether or not to upgrade the virtual machines in your environment, you may analyze and compare the hardware available for various compatibility levels.
vCenter connect
Using the any-to-any vCenter connect functionality, you can manage on-premises and off-premises (cloud providers) vCenter Servers from a single interface.
Read more: Proxmox vs VMware Comparison
VMware vSphere 7 Pricing and Licensing
vSphere 7 is licensed in the vSphere Standard or vSphere Enterprise Plus editions and is licensed per CPU. Each physical processor (CPU) on a server must have at least one processor licensing key assigned to it to run vSphere, which will allow it to run an unrestricted number of VMs.
CPUs with up to 32 physical cores will be covered by each per-processor license. However, additional CPU licenses are necessary if the CPU has more than 32 cores.
VMware vSphere 7 Editions
Licensing keys for vSphere 7 are made up of 25-character alphanumeric strings. When choosing a licensing plan, you have the choice of choosing either Basic Support or Production Support.
There are two licensing editions available.
VMware vSphere Standard
VMware vSphere Standard is an entry-level solution for simple application consolidation, allowing you to save money on hardware while speeding up application deployment. The following are some of the important features of VMware vSphere Standard:
- Image management of next-gen Infrastructure
- Entry-level solution for simple server consolidation
- Includes vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi), vMotion, high availability (HA), and vSphere Replication
- Reduces hardware expenses while speeding application deployment
With basic-level support and a one-year subscription, VMware vSphere 7 Standard costs $1,268. It will cost $1,847.72 if you choose production-level support with a three-year subscription.
VMware vSphere Enterprise Plus
VMware vSphere Enterprise Plus contains the whole set of vSphere capabilities for converting data centers into a simpler cloud operating environment that delivers the next level of speed, security, and simplicity. It includes:
- A comprehensive set of features for converting data centers into cloud infrastructures that are easier to manage
- Use the next generation of flexible, dependable IT services to run modern apps
- Encryption of virtual machine data and drives at rest
- ESXi Hypervisor, vMotion, HA, DRS, vDS, vSphere Trust Authority, vShield Endpoint, VM encryption, and vSphere Replication are all included
VMware vSphere 7 Enterprise Plus starts at $4,350 for a one-year subscription and basic-level support. If you pick production-level support with a three-year subscription, it will cost $5,963.36.
VMware vSphere 7 Pros and Cons
With powerful server virtualization, breakthrough availability, secure automated management, and intelligent operational intelligence that adapts to your environment, VMware vSphere offers business value from day one. Users also have access to preset customizable templates to automate task placement and resource efficiency.
The following are some pros and cons.
Pros
- With over 600,000 clients globally, the most widely used virtualization-layer platform accelerates your digital transformation across every app, any cloud, and any device.
- VMware vSphere 7 offers an easy approach to provide services with almost little downtime.
- The system provides a high level of availability and is simple to migrate from on-premises to any cloud environment.
- A stable and secure administration console for virtual environments is available.
- The most useful feature is VMware Tanzu (container), which provides an effective method for managing VMs and containers in a single pane of glass.
- Businesses can benefit from clustering and quick resource provisioning.
Cons
- Users dislike the underlying hardware’s firmware management.
- The price is higher.
vSphere Use Cases
Virtualizing Business Applications
Virtualizing essential applications on vSphere allows you to make the most of available hardware resources without sacrificing application performance, enables your applications to be more mobile and easily transferred to any server in the environment, and adds an extra layer of baseline availability. It is possible to virtualize:
- Java Applications: Migrate your enterprise Java programs to virtualized x86 platforms to make better use of resources and manage lifecycles and scalability.
- Oracle Databases and Applications: Transform mission-critical Oracle applications, middleware, and databases to a VMware Cloud hybrid or multi-cloud architecture to enable your organization to be more responsive.
- SAP: Increase SAP application availability, provisioning speed with VM clones, and dynamically rebalance apps.
Remote Offices and Branch Offices
Many companies have remote offices and branch offices (ROBOs) with a few servers running workloads. Due to a lack of local IT professionals, uneven host setups, a restricted budget, and limited space, IT support for these locations has unique issues.
With vSphere ROBO, you can manage your distant offices and branch offices with minimal or no local IT employees. It allows for quick server deployment through virtualization as well as reduced host configuration drift and improved regulatory compliance visibility across various sites. You can use VMware ROBO to conduct a variety of tasks, including:
- The VM-level Encryption feature allows users to secure data with encryption.
- Efficient server maintenance on remote hosts can be done with Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) in Maintenance Mode, which automatically takes VMs out of a server when it goes down for maintenance and returns them to the server after the maintenance is completed.
- vSphere vMotion allows live migration of VMs from one physical server to another without causing any downtime.
Disaster Recovery
VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery provides on-demand DRaaS to safeguard a wide range of IT services cost-effectively, while also allowing for quick recovery. In addition, VMware Site Recovery provides hot DRaaS for mission-critical IT services with minimal RPO and RTO requirements.
With disaster recovery, you can protect any workload while balancing the speed and cost of recovery with the criticality of your data.
Is VMware vSphere Right for Your Business?
On modern vSphere infrastructure that enables container-based application development, VMware vSphere manages sophisticated, modern apps as easily as traditional apps and VMs.
You can now upgrade the 70+ million workloads running on vSphere thanks to native Kubernetes architecture. And with vSphere with Tanzu, you can now run new, containerized apps alongside existing enterprise apps on the current infrastructure.
Your infrastructure may be scaled to handle up to 50% additional hosts per cluster, allowing you to meet the needs of high-performance programs, massive virtual machines, and memory-oriented databases. You can also make lifecycle management easier and less disruptive by automating software upgrades, patching, and firmware changes.

