Some things used to be easy. If I paid someone to cut my
grass once a week, they would arrive on that day and take care of it. If they
couldn’t make it, they would call. If I wanted some furniture delivered, we
arranged a day and time, and everything would be there. If I wanted to get long
distance services, I would call the phone company and tell them. They would turn
it on, and it worked.
Some things used to be easy. If I paid someone to cut my grass once a week, they would arrive on that day and take care of it. If they couldnt make it, they would call. If I wanted some furniture delivered, we arranged a day and time, and everything would be there. If I wanted to get long distance services, I would call the phone company and tell them. They would turn it on, and it worked.
Same is true for operating systems. Some of the things that you thought were easy to do in Windows NT 4.0 are
as easy as getting long distance service now in Windows 2000. Remember when you
could just right click on the Network Neighborhood icon, click Properties and
start configuring your network interface properties? Its not quite that easy in
Windows 2000.
The Windows 2000 Router v. Windows NT 4.0 Router
In Windows NT 4.0 you could add a couple of network cards
to your computer and make it a router pretty easily. One of the steps in the process was to go
into the Network Properties dialog box, open the TCP/IP Properties dialog box,
click on the routing tab, and place a checkmark in the checkbox for Enable IP
Forwarding. Just like you see below:
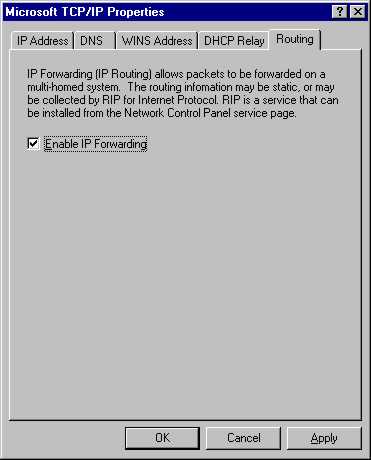
Now, if you mess around in the Windows 2000 Network
Properties dialog boxes for a while, you’ll find nothing that looks like this,
anywhere. That’s because there is no option in Windows 2000 to explicitly
enable IP Forwarding.
Enabling IP Forwarding on the Windows 2000 Server
If you have a Windows 2000 Server family computer, you can
enable IP Forwarding by enabling the Routing and Remote Access Service. After
enabling the service, you need to right click on the Server name in the RRAS
Console, click Properties, and then place a checkmark in the checkbox for Router.
Just like what you see below.
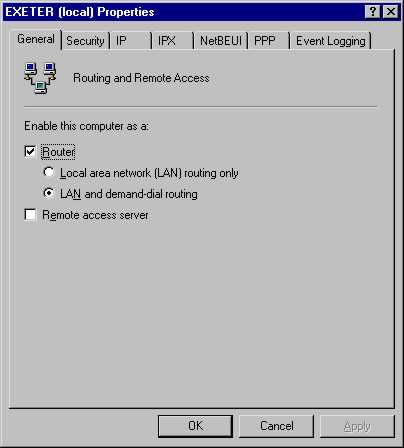
You have now enabled IP Forwarding on your Windows 2000
computer.
What About Windows 2000 Professional?
What about Windows 2000 Professional? Since Windows 2000
Professional is the “big brother” to Windows NT 4.0 Workstation, you
would expect similar functionality, right? But if you look around, you’ll find
that there is no GUI interface that will allow you to enable IP Forwarding. Why?
I suppose Microsoft’s GUI programmers want to keep up with the times, and make
sure that things aren’t as easy as they used to be.
To enable IP Forwarding on a Windows 2000 Professional
computer you need to tweak the registry. This is probably the time to tell you
that if you mess up the registry, bad things can happen. So if you don’t know
what you’re doing, don’t do it!
The registry key and values are:
Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSet
ServicesTcpip Parameters
Value:
IPEnableRouter: REG_DWORD: 0x0
Set the value to 1, and you’ve enabled IP Forwarding on
the Windows 2000 Professional machine. Not quite as easy as it used to be,
right?
For More Information:
For more information on how to configure your Windows 2000
machine for IP Forwarding, check out PSS article ID Q230082.
For more information on the Windows 2000 Router, check out
our Troubleshooting
Windows 2000 TCP/IP book and the Syngress/Osborne
70-216 Study Guide.
Also, be sure to check out the Certification
Emergency Room for more information on this topic and other Windows 2000
MCSE Certification issues.

